Gonorrhea Overview
Gonorrhea, a bacterial infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is an STD that affects around 700,000 people a year in the U.S. Although the official CDC reported numbers are lower at less than 400,000 people in 2010 or 100.8 per 100,000 of the population, it is believed that almost double the amount of people have contracted the disease and are unaware of their condition.
Contracted through sexual contact, including the penis, vagina, anus, and even the mouth and throat, it is easily transmitted from one person to another and when left untreated can cause serious complications in both men and women. In men, the infection can cause a condition called epididymitis, in which the infection spreads to the tubes connected to the testicles, and can be quite painful as well as render a man infertile. In women, the infection can spread to the fallopian tubes and uterus and cause pelvic inflammatory disease. A condition that can cause constant abdominal pain, internal abscesses, as well as render a woman infertile.
Common Symptoms
Gonorrhea symptoms are generally mild to non-existent and are often misconstrued as other less serious health conditions by people when they exhibit them. When there are symptoms they tend to become noticeable between five and thirty days and differ slightly between men and women.
Because the infection is often asymptomatic it is recommended that all sexually active people who are not in monogamous relationships be tested at a minimum of once a year.
If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms you should consult with your physician about possible problems and testing options and refrain from sexual activity.
Common Symptoms In Men May Include:
- Burning sensation when urinating.
- Yellowish white discharge from the penis.
- Painful or swollen testicles.
- A sore throat.

Common Symptoms In Women May Include:
- Burning sensation when urinating.
- Yellowish vaginal discharge.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Painful bowel movements.
Symptoms of the anus are the same between both men and women and may include:
- Itching and burning sensation.
- Yellowish discharge.
- Bleeding.
A gallery of gonorrhea and chlamydia pictures can be found here.
U.S. Statistics by State Age and Gender
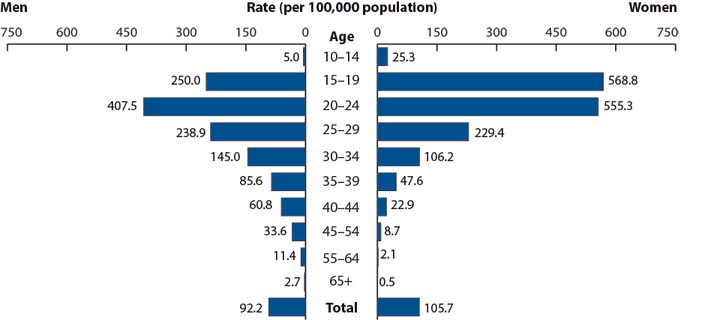
Mandatory reporting of gonorrhea started in 1941 and has been fairly sporadic ever since. The highest number of reported cases was in 1978 with over a million newly infected people or more exactly 459.7 per 100,000 of the population. After which, rates declined until 1997 where they leveled off at below 400,000 new reported infections each year. Keeping in mind that these statistics are only for reported new infections, and that the Center for Disease Control predicts that the actual numbers are most likely double.
As you can see from the age graph above, which holds true with most STD statistics, teens and young adults ages 15 to 24 are the largest demographics that are the most susceptible to infection and is where more attention and education is needed in order to keep infection rates low. Also, noted is the fact that women have a higher rate of infection than men in almost all age groups. In some cases more than double.
2010 Rates per 100,000 by Age Group and Race/Ethnicity
| Age Groups | Asian/Pacific Islanders | American Indians and Alaska Natives | Hispanics | Whites | Blacks |
| 15-24 | 1,130 | 1,560 | 13,935 | 24,722 | 112,230 |
| 25-34 | 738 | 824 | 7,007 | 13,405 | 39,098 |
| 35-44 | 311 | 251 | 2,187 | 5,016 | 9,836 |
| 45-64 | 124 | 97 | 746 | 3,090 | 4,664 |
| Total Averages | 2,303 | 2,732 | 23,875 | 42,233 | 165,828 |
The table above represents reported 2010 data from the Center of Disease Control compiled into race and age groups.
Diagnosis and Treatment Of Gonorrhea
Diagnosis of the STI Gonorrhea can only be done by a physician. If you have any Gonorrhea symptoms you should seek help immediately. In order to check to see if you have gonorrhea online pictures will not do. Your doctor will have to take samples of the infected area (your throat penis or vagina) and send them to a lab to be tested. Sometimes this can be a little uncomfortable especially in men where they may have to swab the inside of the penis.
The Treatment of Gonorrhea is generally quite simple. After being tested, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic which after taking for a certain amount of time will clear up the infection. Gonorrhea used to be easily treated, but is starting to become resistant to certain drugs meaning in the future it may get even harder to treat. When taking the medication make sure to read the instructions on the medication and follow them exactly and remember that after your gonorrhea is treated it can easily be caught again and may become harder to treat the second time.
Untreated Gonorrhea
In women untreated Gonorrhea can develop into Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) which well over 1 million American women have even if they do not know it and have no symptoms. When the symptoms of PID are present they include Stomach pain and Fever. If untreated, PID can damage the fallopian tubes and cause infertility.
In men untreated Gonorrhea can develop into epididymitis (inflammation of the tube at the back of the testicle) A painful disease that swells the testicles and can lead to infertility.
Related Videos on Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea Symptoms, Causes, Effects
Teen Talks About Contracting Gonorrhea